In this series of articles so
far, we have discussed various techniques to identify and exploit
vulnerabilities in Android applications. In the previous article, we
have seen how to exploit debuggable Android applications. In this
article, let’s discuss the vulnerabilities associated with Android
WebViews. Today article is based on how to hack android phone remotely using metasploit in kali linux.

Topics Covered
Introduction to Android WebViews
Implementing WebViews in Android apps
Security issues
Exploiting Android WebView vulnerabilities using Metasploit
Using QR Code attacks
Let’s begin.
Introduction to WebViews
When developing an Android app, we can
load a remote URL or display HTML pages stored in our application within
an activity using WebView. Internally it uses WebKit rendering engine
to display web pages. It supports methods to navigate forward and
backward, text searches, etc. It has some nice features such as support
for the usage of JavaScript.
Implementing WebViews in Android Apps
Implementing WebViews in Android
applications is pretty simple. Initially, we will have to set up all the
required Android project setup like any other Android application
project. Then, we will have to create an object for WebView Class to use
its functionality. Here is a sample code snippet of how we can do this.
In order to load an Internet website:
WebView webview = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.mywebview);
Since we are accessing an Internet
application, we need to have Internet access in order for this to work.
So, we need to request for INTERNET by placing the following line in the
AndroidManifest.xml file:
In order to load a file from the file system:
WebView webview = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.mywebview);
webwiew.loadUrl(“file:///android_asset/www/file.html”);
Security Issues
As mentioned in the beginning, WebView
supports usage of JavaScript. If the application being loaded into
WebView requires JavaScript support, it can be enabled by using the
following line.
WebView webview = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.mywebview);
WebSettings webSettings = myWebView.getSettings();
webSettings.setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
Another powerful feature in WebView is exposing a Java object’s methods to be accessed from JavaScript.
This is one of the important features
which requires a keen eye when implementing, as it can be exploited by
passing malicious JavaScript to the application’s interface. Below is a
sample code snippet by @jduck on how it can be implemented and
exploited.
Exploiting Android WebView Vulnerabilities using Metasploit
In this section, we will see how to
exploit a recent vulnerability which affected most of the Android
devices. This attack works on all the devices running on Android version
4.2 (JellyBean) and earlier.
Launch your Metasploit by typing “msfconsole” in a new terminal.
Type “search android”
to see all the exploits associated with Android. You should see the
screen below (make sure you have updated your Metasploit to see the
screen).
We are going to use the exploit
highlighted in the above figure, which uses vulnerable WebView
components. You can get other information about this exploit by using
the “info” command. 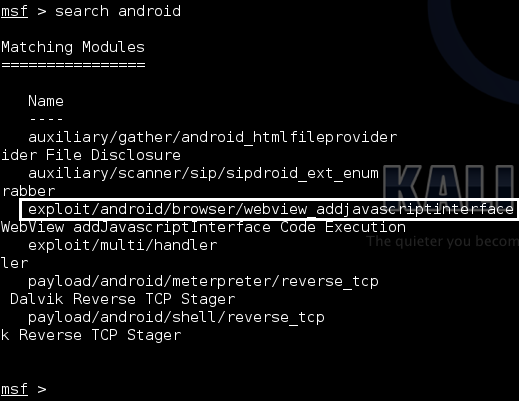
To load the exploit, we can use the command “use ” as shown below.

Now, we can see the options to be set by giving the “show options” command.
IP address and Port to start a reverse handler can be set manually; otherwise it automatically takes the default values.
In our case, we are leaving the default values and setting the URI PATH as shown below.

Once after setting up everything, execute the “exploit” as a command to start a reverse handler.

As we can see in the above figure, a reverse handler has been started at http://192.168.1.104/srini0x00.
We can directly share this URL with the victim. Once he opens it, it
will open up a shell on the device as shown in the figure below.

To make this attack even more
convincing, we can embed the above URL into a QRCode image. If a victim
scans it using a QR code scanner, the URL will automatically pop up and
will be opened in a browser.
This can be achieved using Social Engineering Toolkit.
Steps:
Open up your Social Engineering Toolkit in Kali Linux by following the path given below.
KaliLinux -> Exploitation Tools -> Social Engineering ToolKit -> se-toolkit
Select Social Engineering Attacks followed by QRCode Generator Attack Vector as shown in the figure below.
-
As we can see in the above figure, a QRCode has been generated.
If you go to the location where it is saved, it looks as shown in the figure below.

If a victim scans this QRCode with
QRCode scanner app from his Android device, it will open it up in a
browser and a remote session will be opened in Metasploit.

QRCode opening the URL in a browser
 Session Opened in Metasploit
Session Opened in Metasploit
Let’s have a look at all the active sessions.

Now, let’s start interacting with the session appeared in the previous step. This is shown in the following figure.

I have set my path to system/bin and am now executing the command “cat /proc/cpuinfo” to see the CPU information on the device.

Conclusion-
In this article, we have discussed
attacks associated with WebViews. We can use Drozer for finding and
exploiting these vulnerabilities in Android apps. I have provided a link
as a reference if you are interested to use Drozer for this.




 Session Opened in Metasploit
Session Opened in Metasploit






